| Safe Haskell | None |
|---|---|
| Language | Haskell2010 |
OpenCV.Calib3d
- data FundamentalMatMethod
- data FindHomographyMethod
- data FindHomographyParams = FindHomographyParams {}
- data WhichImage
- findFundamentalMat :: IsPoint2 point2 CDouble => Vector (point2 CDouble) -> Vector (point2 CDouble) -> FundamentalMatMethod -> CvExcept (Maybe (Mat (S '[D, S 3]) (S 1) (S Double), Mat (S '[D, D]) (S 1) (S Word8)))
- findHomography :: IsPoint2 point2 CDouble => Vector (point2 CDouble) -> Vector (point2 CDouble) -> FindHomographyParams -> CvExcept (Maybe (Mat (S '[S 3, S 3]) (S 1) (S Double), Mat (S '[D, D]) (S 1) (S Word8)))
- computeCorrespondEpilines :: IsPoint2 point2 CDouble => Vector (point2 CDouble) -> WhichImage -> Mat (ShapeT [3, 3]) (S 1) (S Double) -> CvExcept (Mat (S [D, S 1]) (S 3) (S Double))
- data SolvePnPMethod
- solvePnP :: forall point3 point2 distCoeffs. (IsPoint3 point3 CDouble, IsPoint2 point2 CDouble, ToMat distCoeffs, MatShape distCoeffs `In` '[S '[S 4, S 1], S '[S 5, S 1], S '[S 8, S 1], S '[S 12, S 1], S '[S 14, S 1]]) => Vector (point3 CDouble, point2 CDouble) -> Mat (ShapeT '[3, 3]) (S 1) (S Double) -> Maybe distCoeffs -> SolvePnPMethod -> CvExcept (Mat (ShapeT '[3, 1]) (S 1) (S Double), Mat (ShapeT '[3, 1]) (S 1) (S Double), Mat (ShapeT '[3, 3]) (S 1) (S Double))
Documentation
data FundamentalMatMethod Source #
Instances
data FindHomographyMethod Source #
Constructors
| FindHomographyMethod_0 | A regular method using all the points. |
| FindHomographyMethod_RANSAC | RANSAC-based robust method. |
| FindHomographyMethod_LMEDS | Least-Median robust method. |
| FindHomographyMethod_RHO | PROSAC-based robust method. |
Instances
data FindHomographyParams Source #
Constructors
| FindHomographyParams | |
Fields
| |
Instances
data WhichImage Source #
Instances
Arguments
| :: IsPoint2 point2 CDouble | |
| => Vector (point2 CDouble) | Points from the first image. |
| -> Vector (point2 CDouble) | Points from the second image. |
| -> FundamentalMatMethod | |
| -> CvExcept (Maybe (Mat (S '[D, S 3]) (S 1) (S Double), Mat (S '[D, D]) (S 1) (S Word8))) |
Calculates a fundamental matrix from the corresponding points in two images
The minimum number of points required depends on the FundamentalMatMethod.
With 7 points the FM_7Point method is used, despite the given method.
With more than 7 points the FM_7Point method will be replaced by the
FM_8Point method.
Between 7 and 15 points the FM_Ransac method will be replaced by the
FM_Lmeds method.
With the FM_7Point method and with 7 points the result can contain up to 3
matrices, resulting in either 3, 6 or 9 rows. This is why the number of
resulting rows in tagged as Dynamic. For all other methods the result always
contains 3 rows.
computeCorrespondEpilines Source #
Arguments
| :: IsPoint2 point2 CDouble | |
| => Vector (point2 CDouble) | Points. |
| -> WhichImage | Image which contains the points. |
| -> Mat (ShapeT [3, 3]) (S 1) (S Double) | Fundamental matrix. |
| -> CvExcept (Mat (S [D, S 1]) (S 3) (S Double)) |
For points in an image of a stereo pair, computes the corresponding epilines in the other image
data SolvePnPMethod Source #
Arguments
| :: (IsPoint3 point3 CDouble, IsPoint2 point2 CDouble, ToMat distCoeffs, MatShape distCoeffs `In` '[S '[S 4, S 1], S '[S 5, S 1], S '[S 8, S 1], S '[S 12, S 1], S '[S 14, S 1]]) | |
| => Vector (point3 CDouble, point2 CDouble) | 3D-2D point correspondences. |
| -> Mat (ShapeT '[3, 3]) (S 1) (S Double) | Camera matrix. |
| -> Maybe distCoeffs | Distortion coefficients. |
| -> SolvePnPMethod | |
| -> CvExcept (Mat (ShapeT '[3, 1]) (S 1) (S Double), Mat (ShapeT '[3, 1]) (S 1) (S Double), Mat (ShapeT '[3, 3]) (S 1) (S Double)) |
Finds an object pose from 3D-2D point correspondences.
Parameters:
objectImageMatches- Correspondences between object coordinate space (3D) and image points (2D).
cameraMatrix- Input camera matrix \[ A = \begin{bmatrix} f_x & 0 & c_x \\ 0 & f_y & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \]
distCoeffs- Input distortion coefficients \( \left ( k_1, k_2, p_1, p_2[, k_3[, k_4, k_5, k_6 [, s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4[, \tau_x, \tau_y ] ] ] ] \right ) \) of 4, 5, 8, 12 or 14 elements. If not given, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
In case of success the algorithm outputs 3 values:
rvec- Output rotation vector that, together with tvec, brings points from the model coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
tvec- Output translation vector.
cameraMatrix- Output camera matrix. In most cases a copy of the input
camera matrix. With the
SolvePnP_UPNPmethod the \(f_x\) and \(f_y\) parameters will be estimated.
The function estimates the object pose given a set of object points, their corresponding image projections, as well as the camera matrix and the distortion coefficients, see the figure below (more precisely, the X-axis of the camera frame is pointing to the right, the Y-axis downward and the Z-axis forward).
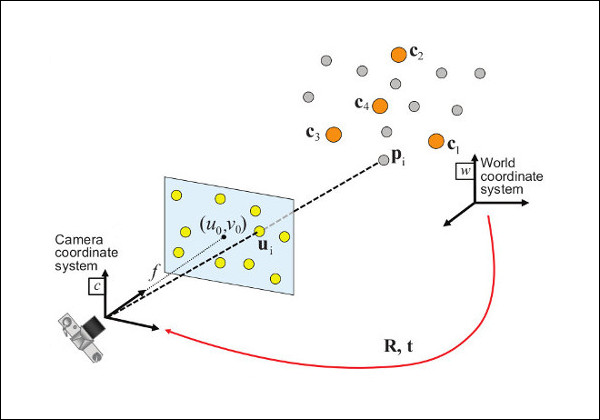
Points expressed in the world frame \(\bf{X_w}\) are projected into the image plane \([u,v]\) using the perspective projection model \(\bf{\Pi}\) and the camera intrinsic parameters matrix \(\bf{A}\):
\[ \begin{align*} \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} &= \bf{A} \hspace{0.1em} \Pi \hspace{0.2em} ^{c}\bf{M}_w \begin{bmatrix} X_{w} \\ Y_{w} \\ Z_{w} \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} &= \begin{bmatrix} f_x & 0 & c_x \\ 0 & f_y & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} & t_x \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} & t_y \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} & t_z \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} X_{w} \\ Y_{w} \\ Z_{w} \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align*} \]
The estimated pose is thus the rotation (rvec) and the translation (tvec) vectors that allow to transform a 3D point expressed in the world frame into the camera frame:
\[ \begin{align*} \begin{bmatrix} X_c \\ Y_c \\ Z_c \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} &= \hspace{0.2em} ^{c}\bf{M}_w \begin{bmatrix} X_{w} \\ Y_{w} \\ Z_{w} \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix} X_c \\ Y_c \\ Z_c \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} &= \begin{bmatrix} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} & t_x \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} & t_y \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} & t_z \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} X_{w} \\ Y_{w} \\ Z_{w} \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align*} \]